5.1.4 Calculus and convex optimization
If some characters seem to be missing, it's because MathJax is not loaded correctly. Refreshing the page should fix it.
- Differentiable functions
- [E] What does it mean when a function is differentiable?
- [E] Give an example of when a function doesn’t have a derivative at a point.
- [M] Give an example of non-differentiable functions that are frequently used in machine learning. How do we do backpropagation if those functions aren’t differentiable?
- Convexity
- [E] What does it mean for a function to be convex or concave? Draw it.
- [E] Why is convexity desirable in an optimization problem?
- [M] Show that the cross-entropy loss function is convex.
Given a logistic discriminant classifier:
where the sigmoid function is given by:
The logistic loss for a training sample with class label is given by:
- Show that .
- Show that .
- Show that is convex.
Most ML algorithms we use nowadays use first-order derivatives (gradients) to construct the next training iteration.
- [E] How can we use second-order derivatives for training models?
- [M] Pros and cons of second-order optimization.
- [M] Why don’t we see more second-order optimization in practice?
- [M] How can we use the Hessian (second derivative matrix) to test for critical points?
- [E] Jensen’s inequality forms the basis for many algorithms for probabilistic inference, including Expectation-Maximization and variational inference.. Explain what Jensen’s inequality is.
- [E] Explain the chain rule.
- [M] Let , in which is a one-hot vector. Take the derivative of with respect to .
- [M] Given the function with the constraint . Find the function’s maximum and minimum values.
On convex optimization
Convex optimization is important because it's the only type of optimization that we more or less understand. Some might argue that since many of the common objective functions in deep learning aren't convex, we don't need to know about convex optimization. However, even when the functions aren't convex, analyzing them as if they were convex often gives us meaningful bounds. If an algorithm doesn't work assuming that a loss function is convex, it definitely doesn't work when the loss function is non-convex.
Convexity is the exception, not the rule. If you're asked whether a function is convex and it isn't already in the list of commonly known convex functions, there's a good chance that it isn't convex. If you want to learn about convex optimization, check out Stephen Boyd's textbook.
On Hessian matrix
The Hessian matrix or Hessian is a square matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a scalar-valued function.
Given a function . If all second partial derivatives of f exist and are continuous over the domain of the function, then the Hessian matrix H of f is a square nn matrix such that: .
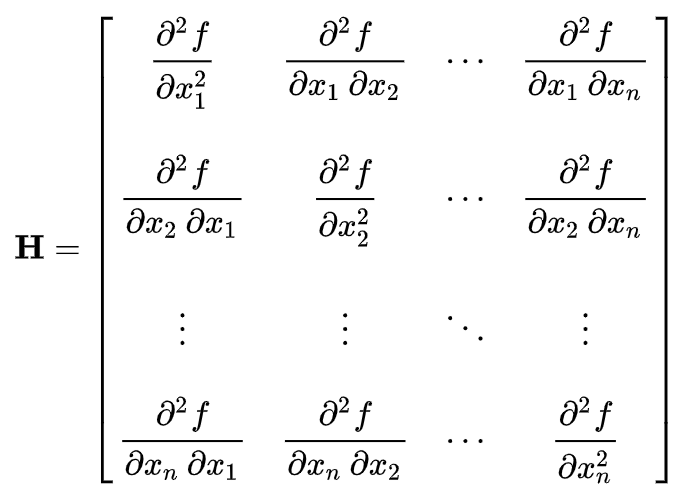
The Hessian is used for large-scale optimization problems within Newton-type methods and quasi-Newton methods. It is also commonly used for expressing image processing operators in image processing and computer vision for tasks such as blob detection and multi-scale signal representation.